A hybrid elastic band string algorithm for studies of enzymatic reactions
Abstract
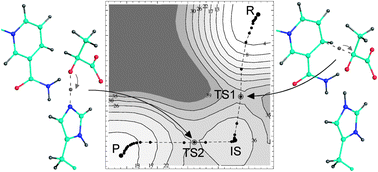
A common challenge in theoretical biophysics is the identification of a minimum energy path (MEP) for the rearrangement of a group of atoms from one stable configuration to another. The structure with maximum energy along the MEP approximates the transition state for the process and the energy profile itself permits estimation of the transition rates. In this work we describe a computationally efficient algorithm for the identification of minimum energy paths in complicated biosystems. The algorithm is a hybrid of the nudged elastic band (NEB) and string methods. It has been implemented in the pDynamo simulation program and tested by examining elementary steps in the reaction mechanisms of three enzymes: citrate synthase, RasGAP, and lactate dehydrogenase. Good agreement is found for the energies and geometries of the species along the reaction profiles calculated using the new algorithm and previous versions of the NEB and string techniques, and also those obtained by the common method of adiabatic exploration of the potential energy surface as a function of predefined reaction coordinates. Precisely refined structures of the saddle points along the paths may be subsequently obtained with the climbing image variant of the NEB algorithm. Directions in which the utility of the methods that we have implemented can be further improved are discussed.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Theoretical chemical physics of biological systems

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...