Proton-coupled hole hopping in nucleosomal and free DNA initiated by site-specific hole injection†
Abstract
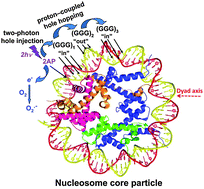
Nucleosomes were reconstituted from recombinant histones and a 147-mer DNA sequence containing the damage reporter sequence 5′-…d([2AP]T[GGG]1TT[GGG]2TTT[GGG]3TAT)… with 2-aminopurine (2AP) at position 27 from the dyad axis. Footprinting studies with ˙OH radicals reflect the usual effects of “in” and “out” rotational settings, while, interestingly, the guanine oxidizing one-electron oxidant CO3˙− radical does not. Site-specific hole injection was achieved by 308 nm excimer laser pulses to produce 2AP˙+ cations, and superoxide via the trapping of hydrated electrons. Rapid deprotonation (∼100 ns) and proton coupled electron transfer generates neutral guanine radicals, G(–H)˙ and hole hopping between the three groups of [GGG] on micro- to millisecond time scales. Hole transfer competes with hole trapping that involves the combination of O2˙− with G(–H)˙ radicals to yield predominantly 2,5-diamino-4H-imidazolone (Iz) and minor 8-oxo-7,8-dihydroguanine (8-oxoG) end-products in free DNA (Misiaszek et al., J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 32106). Hole migration is less efficient in nucleosomal than in the identical protein-free DNA by a factor of 1.2–1.5. The Fpg/piperidine strand cleavage ratio is ∼1.0 in free DNA at all three GGG sequences and at the “in” rotational settings [GGG]1,3 facing the histone core, and ∼2.3 at the “out” setting at [GGG]2 facing away from the histone core. These results are interpreted in terms of competitive reaction pathways of O2˙− with G(–H)˙ radicals at the C5 (yielding Iz) and C8 (yielding 8-oxoG) positions. These differences in product distributions are attributed to variations in the local nucleosomal B-DNA base pair structural parameters that are a function of surrounding sequence context and rotational setting.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...