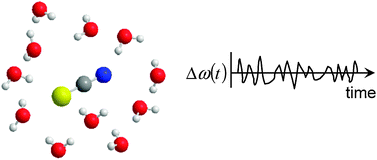
In this paper, we report on our investigation into the vibrational dynamics of the antisymmetric stretching modes of SCN− and N3− in several polar solvents. We used an infrared (IR) pump–probe method to study orientational relaxation processes. In two aprotic solvents (N,N-dimethylformamide (DMF) and dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO)), the anisotropy decay shows a bimodal feature, whereas in other solvents the anisotropy decay can be fitted well by a single exponential function. We consider that the relative contribution of fast-decaying components is smaller in the other solvents than in DMF and DMSO. We discuss the possible origins of the different anisotropy decay behavior in different solvents. From the three-pulse IR photon echo measurements for SCN− and N3−, we found that the time-correlation functions (TCFs) of vibrational frequency fluctuations decay on two different time scales, one of which is less than 100 fs and the other is approximately 3–6 ps. In aprotic solvents, the fast-decaying components of the TCFs on a <100 fs time scale play an important role in the vibrational frequency fluctuation, although the contribution of collective solvent reorganization in aprotic solvents was clearly observed to have small amplitudes. On the other hand, we found that the amplitude of components that decay in a few picoseconds and/or the constant offset of the TCF in protic solvents is relatively large compared with that in aprotic solvents. With the formation and dissociation of hydrogen bonds between ion solute and solvent molecules, the spectra of different solvated species are exchanged with each other and merged into one band. We considered that this exchange may be an origin of slow-decaying components of the TCFs and that the decay of the TCFs corresponds to the time scales of the exchange for protic solvents such as formamide. The mechanism of vibrational frequency fluctuations for the antisymmetric stretching modes of SCN− and N3− is discussed in terms of the difference between protic and aprotic solvents.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...