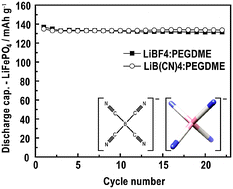
The role of B(CN)4− (Bison) as a component of battery electrolytes is addressed by investigating the ionic conductivity and phase behaviour of ionic liquids (ILs), ion association mechanisms, and the electrochemical stability and cycling properties of LiBison based electrochemical cells. For C4mpyrBison and C2mimBison ILs, and mixtures thereof, high ionic conductivities (3.4 ≤ σion ≤ 18 mS cm−1) are measured, which together with the glass transition temperatures (−80 ≤ Tg ≤ −76 °C) are found to shift systematically for most compositions. Unfortunately, poor solubility of LiBison in these ILs hinders their use as solvents for lithium salts, although good NaBison solubility offers an alternative application in Na+ conducting electrolytes. The poor IL solubility of LiBison is predicted to be a result of a preferred monodentate ion association, according to first principles modelling, supported by Raman spectroscopy. The solubility is much improved in strongly Li+ coordinating oligomers, for example polyethylene glycol dimethyl ether (PEGDME), with the practical performance tested in electrochemical cells. The electrolyte is found to be stable in Li/LiFePO4 coin cells up to 4 V vs.Li and shows promising cycling performance, with a capacity retention of 99% over 22 cycles.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...