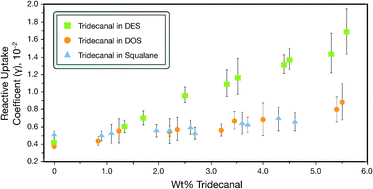
We report the first measurements of the reactive uptake of NO3 with condensed-phase aldehydes. Specifically, we studied NO3 uptake on solid tridecanal and the uptake on liquid binary mixtures containing tridecanal and saturated organic molecules (diethyl sebacate, dioctyl sebacate, and squalane) which we call matrix molecules. Uptake on the solid was shown to be efficient, where γ = (1.6 ± 0.8) × 10−2. For liquid binary mixtures the reactivity of aldehyde depended on the matrix molecule. Assuming a bulk reaction, 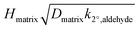 varied by a factor of 2.6, and assuming a surface reaction
varied by a factor of 2.6, and assuming a surface reaction 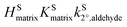 varied by a factor of 2.9, where
varied by a factor of 2.9, where 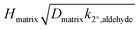 and
and 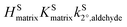 are constants extracted from the data using the resistor model. By assuming either a bulk or surface reaction, the atmospheric lifetimes for aldehydes were estimated to range from 1.9–7.5 h. We also carried out detailed studies of N2O5 uptake kinetics on alcohols. We show that uptake coefficients of N2O5 for five different organics at 293 K varied by more than 2 orders of magnitude, ranging from 3 × 10−4 to 1.8 × 10−2. We show that the uptake coefficients correlate with
are constants extracted from the data using the resistor model. By assuming either a bulk or surface reaction, the atmospheric lifetimes for aldehydes were estimated to range from 1.9–7.5 h. We also carried out detailed studies of N2O5 uptake kinetics on alcohols. We show that uptake coefficients of N2O5 for five different organics at 293 K varied by more than 2 orders of magnitude, ranging from 3 × 10−4 to 1.8 × 10−2. We show that the uptake coefficients correlate with 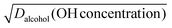 but more work is needed with other alcohols to completely understand the dependence. Using this kinetic data we show that the atmospheric lifetime of alcohols with respect to N2O5 heterogeneous chemistry can vary from 0.6–130 h, depending on the physical and chemical properties of the organic liquid.
but more work is needed with other alcohols to completely understand the dependence. Using this kinetic data we show that the atmospheric lifetime of alcohols with respect to N2O5 heterogeneous chemistry can vary from 0.6–130 h, depending on the physical and chemical properties of the organic liquid.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
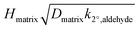 varied by a factor of 2.6, and assuming a surface reaction
varied by a factor of 2.6, and assuming a surface reaction 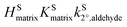 varied by a factor of 2.9, where
varied by a factor of 2.9, where 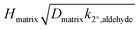 and
and 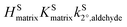 are constants extracted from the data using the resistor model. By assuming either a bulk or surface reaction, the atmospheric lifetimes for
are constants extracted from the data using the resistor model. By assuming either a bulk or surface reaction, the atmospheric lifetimes for 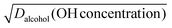 but more work is needed with other
but more work is needed with other 

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...