The electro-oxidation of formate ions at a polycrystalline Pt electrode in alkaline solution: an in situFTIR study
Abstract
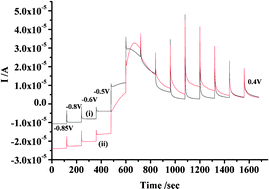
This paper reports in situFTIR studies on the oxidation of formate at polycrystalline Pt in aqueous
* Corresponding authors
a School of Chemical Engineering and Advanced Materials, Bedson Building, Newcastle University, Newcastle upon Tyne, England, UK
This paper reports in situFTIR studies on the oxidation of formate at polycrystalline Pt in aqueous

 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
P. A. Christensen, A. Hamnett and D. Linares-Moya, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2011, 13, 11739 DOI: 10.1039/C1CP20166B
This is an Open Access article. The full version of this article can be posted on a website/blog, posted on an intranet, photocopied, emailed, distributed in a course pack or distributed in Continuing Medical Education (CME) materials provided that it is not used for commercial purposes.
To request permission to reproduce material from this article in a commercial publication, please go to the Copyright Clearance Center request page.
If you are an author contributing to an RSC publication, you do not need to request permission provided correct acknowledgement is given.
If you are the author of this article, you do not need to request permission to reproduce figures and diagrams provided correct acknowledgement is given. If you want to reproduce the whole article in a third-party commercial publication (excluding your thesis/dissertation for which permission is not required) please go to the Copyright Clearance Center request page.
Read more about how to correctly acknowledge RSC content.
 Fetching data from CrossRef.
Fetching data from CrossRef.
This may take some time to load.
Loading related content
