Effect of the chemical composition on the work function of gold substrates modified by binary self-assembled monolayers
Abstract
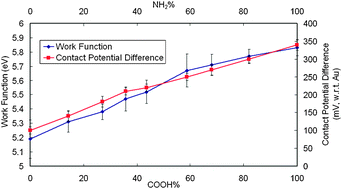
This study demonstrated that the work function (Φ) of Au substrates can be fine-tuned by using series ratios of binary self-assembled monolayers (SAMs). By using pure

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...