The rotational excitation of the interstellar HNC by para- and ortho-H2
Abstract
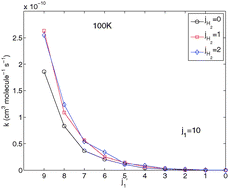
Rotational excitation of the interstellar HNC due to collisions with H2 is investigated. We present a new four dimensional (4D) potential energy surface for the HNC–H2 collisional system. Both molecules were treated as rigid rotors. Interaction energy was obtained from the electronic structure calculations using a single and double-excitation coupled cluster method with perturbative contributions from connected triple excitations [CCSD(T)]. The five atoms were described using the aug-cc-pVTZ basis sets. Bond functions were placed at mid-distance between the HNC center of mass and the center of mass of H2 for a better description of the van der Waals interaction. Close coupling calculations of the inelastic integral cross sections of HNC in collisions with para-H2 and ortho-H2 were calculated for kinetic energies up to 800 cm−1. After Boltzmann thermal averaging, rate coefficients were obtained for temperatures ranging from 5 to 100 K. Significant differences exist between para- and ortho-H2 results. The strongest collision-induced rotational HNC transitions are the transitions with Δj = 1 for collisions with para-H2 and with ortho-H2. The new rate coefficients should induce important consequences on the determination of HNC abundance in the interstellar medium. In particular, we expect that they will help to solve the interstellar problem of relative abundance of the HCN and HNC isomers.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Molecular Collision Dynamics

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...