Novel view on the mechanism of water-assisted proton transfer in the DNA bases: bulk water hydration
Abstract
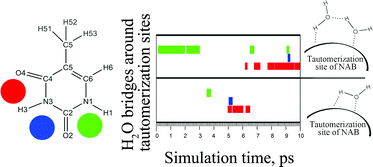
In the present work, the conventional static ab initio picture of a water-assisted mechanism of the tautomerization of Nucleic Acid Bases (NABs) in an aqueous environment is enhanced by the classical and Car–Parrinello molecular dynamics simulations. The inclusion of the dynamical contribution is vital because the formation and longevity of the NAB–water bridge complexes represent decisive factors for further tautomerization. The results of both molecular dynamic techniques indicate that the longest time when such complexes exist is significantly shorter than the time required for

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...