Thermoresponsive, spin-labeled hydrogels as separable DNP polarizing agents†
Abstract
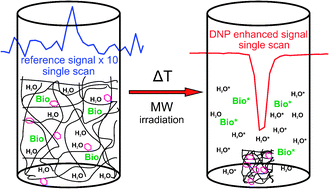
In this work, we present thermoresponsive, spin-labeled hydrogels that bear great potential for applications in dynamic nuclear polarization (DNP). In our approach, the
- This article is part of the themed collection: High field dynamic nuclear polarization – The renaissance

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...