Sulfur poisoning mechanism of steam reformingcatalysts: an X-ray absorption near edge structure (XANES) spectroscopic study†
Abstract
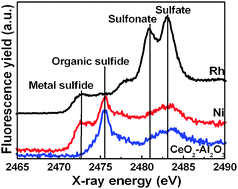
The present XANES study aims at elucidating the roles of
- This article is part of the themed collection: Recent developments in X-ray absorption spectroscopy

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...