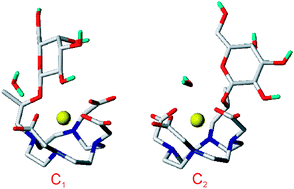
The conformational behaviour in aqueous solution of the EgadMe complex, a conditional gadolinium-based contrast agent sensitive to β-galactosidase enzymatic activity, is investigated by means of ab initio calculations and classical molecular dynamics simulations. Furthermore, force field parameterization of gadolinium–ligand interactions is performed, and its reliability is tested on the bench mark [Gd(DOTA)]− system by MD simulations. Both computational methods highlight the presence in EgadMe of two main conformational isomers. The lowest energy conformation is a “close” form, corresponding to a state of low-relaxivity (MRI “inactive”), in which the ninth coordination site of the gadolinium ion is occupied by one oxygen atom of the galactopyranose residue. The second isomer, which is 2.9 (at ab initio level) and 4.2 (at MD level) kcal mol−1 above the global minimum, presents an “open” form, corresponding to a state of high-relaxivity (MRI “active”) in which one water molecule coordinates the ion. These results are consistent with experimental findings reported for EgadMe, and show that competition at the ninth coordination site of gadolinium ion, between the intra (the galactopyranose residue) and inter (water molecules) molecular interactions, affects the relaxivity of this system.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...