Computing free energies of interfaces in self-assembling systems
Abstract
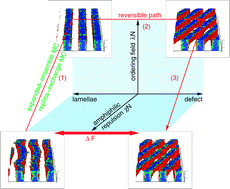
Using molecular simulation of a coarse-grained model for a symmetric
- This article is part of the themed collection: Coarse-grained modeling of soft condensed matter

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...