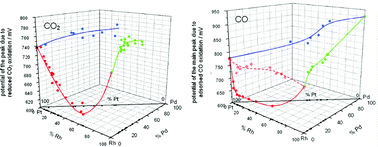
CO2 reduction and CO adsorption on noble metals (Pt, Rh, Pd) and their alloys (Pt–Rh, Pd–Pt, Pd–Rh, Pd–Pt–Rh) prepared as thin rough deposits have been studied by chronoamperometry (CA), cyclic voltammetry (CV) and the electrochemical quartz crystal microbalance (EQCM). The influence of alloy surface composition on the values of surface coverage, eps (electron per site) and potential of the oxidation of CO2 reduction and CO adsorption products is shown. The oxidation of the adsorbate on Pt–Rh alloys proceeds more easily (at lower potentials) than on pure metals. On the other hand, in the case of Pd–Pt and Pd–Rh alloys the adsorbate oxidation is more difficult and requires higher potentials than on Pt or Rh. The analysis of the EQCM signal is presented for the case of adsorption and oxidation of carbon oxide adsorption products on the electrodes studied. The comparison of adsorption parameters and the EQCM response obtained for platinum group metals and alloys leads to the conclusion that reduced CO2 cannot be totally identified with adsorbed CO.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...