Interfacial rheology of stable and weakly aggregated two-dimensional suspensions
Abstract
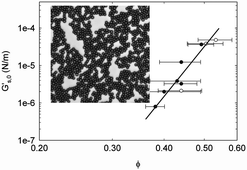
The interfacial rheological properties of stable and weakly aggregated two-dimensional suspensions are studied experimentally using a magnetic rod interfacial rheometer. Particle monolayers with well controlled structures were prepared. Charged polystyrene particles create two-dimensional colloidal crystals at the water–decane interface over a wide range of concentrations. Under similar conditions a predominantly liquid structure is obtained at the water–air interface for the same particles. The addition of appropriate combinations of the anionic

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...