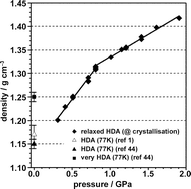
We report in situ density values of amorphous ice obtained between 0.3 and 1.9 GPa and 144 to 183 K. Starting from high-density amorphous ice made by pressure-amorphizing hexagonal ice at 77 K, samples were heated at a constant pressure until crystallization to high-pressure ices occurred. Densities of amorphous ice were calculated from those of high-pressure ice mixtures and the volume change on crystallization. In the density versus pressure plot a pronounced change of slope occurs at ∼0.8 GPa, with a slope of 0.21 g cm−3 GPa−1 below 0.8 GPa and a slope of 0.10 g cm−3 GPa−1 above 0.8 GPa. Both X-ray diffractograms and Raman spectra of recovered samples show that major structural changes occur up to ∼0.8 GPa, developing towards those of very high-density amorphous ice reported by (T. Loerting, C. Salzmann, I. Kohl, E. Mayer and A. Hallbrucker, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2001, 3, 5355) and that further increase of pressure has only a minor effect. In addition, the effect of annealing temperature (TA) at a given pressure on the structural changes was studied by Raman spectra of recovered samples in the coupled O–H and decoupled O–D stretching band region: at 0.5 GPa structural changes are observed between ∼100–116 K, at 1.17 GPa between ∼121–130 K. Further increase of TA or of annealing time has no effect, thus indicating that the samples are fully relaxed. We conclude that mainly irreversible structural changes between 0.3 to ∼0.8 GPa lead to the pronounced increase in density, whereas above ∼0.8 GPa the density increase is dominated to a large extent by reversible elastic compression. These results seem consistent with simulation studies by (R. Martoňàk, D. Donadio and M. Parrinello, J. Chem. Phys., 2005, 122, 134501) where substantial reconstruction of the topology of the hydrogen bonded network and changes in the ring statistics from e.g. mainly six-membered to mainly nine-membered rings were observed on pressure increase up to 0.9 GPa and further pressure increase had little effect.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...