Infrared emission spectra and equilibrium bond lengths of gaseous ZnH2 and ZnD2Electronic supplementary information (ESI) available: A complete list of the observed line positions and the outputs of least-squares fitting program (Tables S1–S13). See http://dx.doi.org/10.1039/b507539d
Abstract
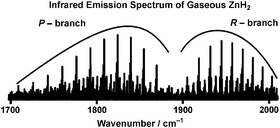
A detailed analysis of the high resolution infrared emission spectra of gaseous ZnH2 and ZnD2 in the 800–2200 cm−1 spectral range is presented. The ν3 antisymmetric stretching fundamental bands of 64ZnH2, 66ZnH2, 67ZnH2, 68ZnH2, 64ZnD2, 66ZnD2 and 68ZnD2, as well as several hot bands involving ν1, ν2 and ν3 were rotationally analyzed, and spectroscopic constants were obtained. Rotational l-type doubling and l-type resonance, local perturbations, and Fermi resonances were observed in the vibration–rotation bands of both ZnH2 and ZnD2, and equilibrium vibrational frequencies (ω1, ω2 and ω3) were estimated. Using the rotational constants of the 000, 100, 0110 and 001 vibrational levels, the equilibrium rotational constants (Be) of 64ZnH2 and 64ZnD2 were determined to be 3.600 269(31) cm−1 and 1.801 985(25) cm−1, respectively, and the associated equilibrium bond lengths (re) are 1.524 13(1) Å and 1.523 94(1) Å, respectively. The difference between the re values of 64ZnH2 and 64ZnD2 is about 0.01%, and is mainly due to the breakdown of the Born–Oppenheimer approximation.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...