Nucleation front instability in two-dimensional (2D) nanosheet gadolinium-doped cerium oxide (CGO) formation
Abstract
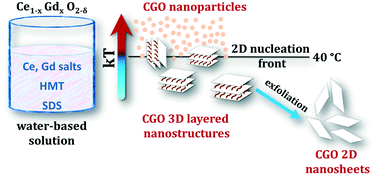
Herein we report for the first time the synthesis of ceramic–organic three-dimensional (3D) layered gadolinium-doped cerium oxide (Ce1−XGdXO2−δ, CGO) and its exfoliation into two-dimensional (2D) nanosheets. We adopt a water-based synthetic route via a homogenous precipitation approach at low temperatures (10–80 °C). The reaction conditions are tuned to investigate the effects of thermal energy on the final morphology. A low temperature (40 °C) morphological transition from nanoparticles (1D) to two-dimensional (2D) nanosheets is observed and associated with a low thermal energy transition of ca. 2.6 kJ mol−1. For the 3D-layered material, exfoliation experiments are conducted in water/ethanol solutions. Systems at volume fractions ranging from 0.15 to 0.35 are demonstrated to promote under ultrasonic treatment the delamination into 2D nanosheets.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...