Development of a Wattecs parallel autoclave system synthesis technique for tailoring surface compositions and valence states of Pt–Fe alloys to realize bifunctional electrocatalysis†
Abstract
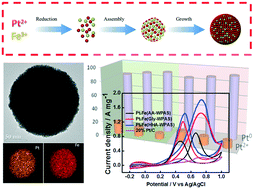
The development of bifunctional electrocatalysts for both the methanol oxidation reaction (MOR) at the anode and the oxygen reduction reaction (ORR) at the cathode is urgently required for promoting electrochemical energy conversion and lowering the cost of fuel cells. The surface electron configuration, correlated to the surface elemental composition and the valence state of an electrocatalyst plays crucial roles in achieving bifunctionality and efficient electrocatalysis. In this study, we demonstrate the achievement of bifunctional Pt–Fe alloy electrocatalysts for effectively catalyzing both the MOR and ORR by tailoring their surface electron configuration via a synthetic strategy employing a Wattecs parallel autoclave system (WPAS), which allows the alteration of reaction atmospheres and operating conditions during the synthetic process, in contrast to a normal hydrothermal method. The optimal Pt–Fe alloy electrocatalyst displayed remarkably enhanced ORR electrocatalytic performance with a half-potential (E1/2) of 0.9 V (vs. Ag/AgCl), together with robust stability (3000 cycles), in the ORR in a 0.1 M HClO4 solution and exhibited excellent catalytic performance in the MOR with a mass activity of 1.82 A mg−1, which is 7.9 times higher than that of commercial 20% Pt/C (0.23 A mg−1). These Pt–Fe alloy electrocatalysts also possessed long-term stability and the ability to tolerate CO intermediates and hold great significance for widespread applications in the field of renewable energy owing to their low cost and superior bifunctionality for both the MOR and ORR. The variability of the surface electron configuration that arose from the purposive modulation of the chemical composition and valence state of the surface of the Pt–Fe alloy electrocatalysts accounted for the increase in electrocatalytic performance and the achievement of bifunctional catalysis in both the MOR and ORR.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...