A Cd mixed-ligand MOF showing ligand-disorder induced breathing behaviour at high temperature and stepwise, selective carbon dioxide adsorption at low temperature†
Abstract
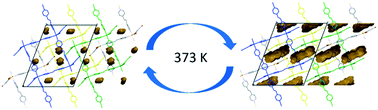
A mixed-ligand MOF [Cd(bpe)1.5(nbdc)]n·nDMF0.84 (1) has been synthesized where bpe = 1,2-bis(4-pyridyl)ethane, nbdc = 5-nitro-1,3-benzenedicarboxylate and DMF = N,N′-dimethylformamide. Single crystal X-ray diffraction studies reveal that the structure consists of 2-periodic, 3D nets which exhibit a square lattice motif and are catenated throughout the crystal structure. Variable-temperature single crystal X-ray diffraction studies show that the desolvation of the crystal upon heating is a single-crystal-to-single-crystal (SCSC) process accompanied by a change in the lattice constants, crystal system and space group. Disorder of the axial bpe ligands provide useful insight into the path of desolvation and also indicates that the relative void space at high temperature changes dynamically by nearly 600%, indicating a temperature-induced ‘breathing’ effect. Compound 1 shows appreciable sorption of carbon dioxide at 273 K and shows significantly increased sorption at 195 K with an associated change in the sorption profile, indicative of structural changes. The compound also adsorbed water vapour (298 K) to an appreciable amount.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...