Synthesis of monodispersed colloidal particles via a hydrothermally promoted double hydrolysis approach
Abstract
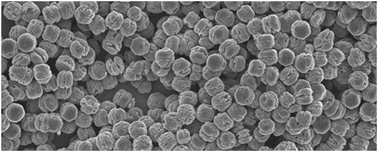
Monodispersed colloidal particles have received continuously increasing attention due to their unique physicochemical properties for applications in many technological areas, especially in nanotechnology. The size and morphology of the colloid particles produced in a homogeneous solution are very sensitive to the synthesis conditions. Thus, it has been a great challenge to generalize the synthesis of monodispersed colloidal particles. In this work, a hydrothermally promoted double hydrolysis approach (HPDH) was found to be effective in the synthesis of monodispersed colloidal particles of different compositions. Several types of colloids were synthesized to demonstrate the feasibility and versatility of this novel approach. The monodispersity of the colloids was examined by scanning electron microscopy, transmission electron microscopy and particle size distribution analysis. The crystalline structure and porosity of the colloids were investigated by X-ray diffraction, selected area-electron diffraction and N2 adsorption methods. Results show that the HPDH derived colloids have a high monodispersity, which may render these materials highly potential in numerous emerging applications.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...