Role of polymers in solution and tablet-based carbamazepine cocrystal formulations†
Abstract
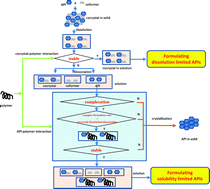
The aim of this study was to evaluate the influence of three chemically diverse polymers, namely hydroxypropylmethylcellulose acetate succinate (HPMCAS), polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP) and polyethylene glycol (PEG) on the phase transformation of three carbamazepine (CBZ) cocrystals including carbamazepine–nicotinamide (CBZ–NIC), carbamazepine–saccharin (CBZ–SAC) and carbamazepine–cinnamic acid (CBZ–CIN) in solution and tablet-based formulations. Based on the solubility and powder dissolution studies, it is demonstrated that cocrystals can be easily formulated through a simple solution formulation or powder formulation to generate supersaturated concentrations and faster dissolution rates to overcome those drugs with solubility and/or dissolution limited bioavailability. However, a polymer-based CBZ cocrystal tablet formulation has not shown any advantage of an improved CBZ release rate compared with the formulation of CBZ III or physical mixtures of CBZ III and coformers. This is in contrast to the solution behaviours of CBZ cocrystals in the solubility and powder dissolution tests because crystallization of the stable solid form of CBZ dihydrate (CBZ DH) within the tablet has taken place, leading to a reduced drug release rate and incomplete release. The mechanism of a polymer inhibition effect on drug precipitation in solution has been elucidated through investigating the molecular interactions among CBZ, coformers and polymers in solution using infrared spectroscopy. Finally, a formulation strategy has been proposed to capture the significant advantages of cocrystals.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...