Synthesis and formation mechanisms of morphology-controllable indium-containing precursors and optical properties of the derived In2O3 particles†
Abstract
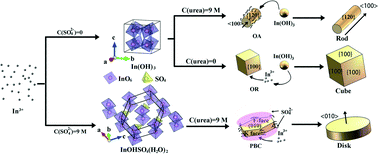
In2O3 particles with three distinctive morphologies of 1D rods, 2D disks and 3D cubes were converted from their respective precursors synthesized by a facile urea-based homogeneous precipitation method. Two kinds of precursor phases, including In(OH)3 and InOHSO4(H2O)2, were obtained. In the case of high urea concentration, mesocrystalline rod-like In(OH)3 particles were produced by oriented primary particle aggregation induced by the coordination of urea on {012} of the primary particles. In contrast, cube-like In(OH)3 was obtained by Ostwald ripening in low-concentration urea solution. The addition of K2SO4 facilitates the formation of an In–sulfate complex, and InOHSO4(H2O)2 precursor disks about 2 μm in diameter were formed. It is suggested that the adsorption of urea on the active growth sites of the precursor leads to the formation of round disks instead of hexagonal plates. Upon blue light excitation, the three types of In2O3 particles obtained from their respective precursors exhibited a morphology-dependent photoluminescence behavior (disks > cubes > rods), but did not differ greatly in the positions of the PLE and PL bands of the luminescence. The emission (in the range of 500–540 nm) from In2O3 is associated with oxygen vacancies and is highly dependent on the annealing atmosphere.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...