Facile synthesis of Fe-containing metal–organic frameworks as highly efficient catalysts for degradation of phenol at neutral pH and ambient temperature†
Abstract
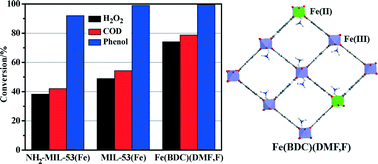
In this work, MIL-53(Fe) was synthesized using a solvothermal method under static conditions. However, it was interesting to find that another MIL-53 type material, Fe(BDC)(DMF,F), was obtained when stirring conditions were used while keeping the other conditions fixed. The Fe-containing metal–organic frameworks (MOFs) were characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), 57Fe Mössbauer spectrometry and thermogravimetric analysis (TGA). By simply increasing the crystallization time under agitation, the morphology of the Fe(BDC)(DMF,F) crystals went through a striking transition from a bulky irregular shape to a rod-like morphology. The catalytic performance of the Fe-MOFs was evaluated in the degradation of phenol solution at near neutral pH at 35 °C. A significantly better catalytic activity was achieved for Fe(BDC)(DMF,F) than for MIL-53(Fe) and NH2-MIL-53(Fe) due to the existence of Fe(II) in its framework. Phenol was almost completely decomposed in 3 hours, and the conversions of hydrogen peroxide and chemical oxygen demand (COD) were 74.1% and 78.7%, respectively.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...