Developmental considerations for ethanolates with regard to stability and physicochemical characterization of efonidipine hydrochloride ethanolate†
Abstract
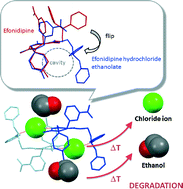
Efonidipine hydrochloride ethanolate (NZ-105) is a novel 1,4-dihydropyridine derivative and Ca antagonist. Its chemical structure is distinctive, being a solvate composed of an equimolar adduct of ethanol and efonidipine hydrochloride, and it represents one of a few cases of solvates marketed as a pharmaceutical drug. The research presented in this paper used methods to assess its solid-state properties and included thermal analysis (thermogravimetry-differential thermal analysis, TG-DTA), Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FT/IR), evolved gas analysis-mass spectrometry (EGA-MS), environmental (low-vacuum) scanning electron microscopy (E-SEM), variable temperature powder X-ray diffraction, and single-crystal X-ray structure analysis, in order to clarify the thermal behavior of the hydrogen chloride and ethanol adducts of efonidipine in the study of the thermal stability of efonidipine hydrochloride ethanolate. Upon heating, efonidipine hydrochloride ethanolate first released ethanol and subsequently formed a decomposition product with the elimination of chloride ions. X-ray diffraction patterns and particulate forms were markedly altered after the release of ethanol, which suggested the interaction of ethanol molecules with chloride ions and efonidipine molecules within the crystal structure. Vastly different from efonidipine, the crystal structure of efonidipine hydrochloride ethanolate arranges the chloride ion within a basket-type conformation formed by the bulky diphenyl and phosphate groups. This distinctive crystal structure was thought to suppress the elimination of chloride ions and contribute significantly to the improved thermal stability of the compound.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...