Structural diversity of 5-methylnicotinate coordination assemblies regulated by metal-ligating tendency and metal-dependent anion effect†
Abstract
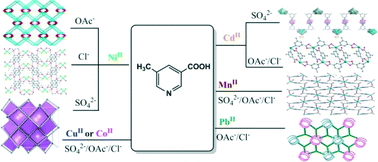
Nine 5-methylnicotinate (L–CH3−) coordination complexes, namely, {[Ni(L–CH3)2(H2O)2](H2O)}n (1), [Ni2(L–CH3)4(H2O)]n (2), Ni(HL–CH3)2Cl2 (3), [Cd2(L–CH3)2(SO4)(H2O)6]n (4), [Cd(L–CH3)2(H2O)]n (5), {[Cu(L–CH3)2(H2O)2](H2O)}n (6), {[Co(L–CH3)2(H2O)2](H2O)}n (7), [Mn(L–CH3)2(H2O)2]n (8), and [Pb(L–CH3)2]n (9), were synthesized with different metal salts. For complexes 1–3, the use of different NiII salts (SO42−, OAc−, or Cl−) leads to three distinct coordination motifs, including a 3D lvt framework, a 3D self-interpenetrating (3·4·5)(32·43·53·6·74·82) network, and a mononuclear species, respectively. For CdII, two different 1D chain complexes can be assembled from HL–CH3 with CdSO4 (4) and Cd(OAc)2 or CdCl2 (5). However, such an anion effect has not been observed for the CuII (6), CoII (7), MnII (8), and PbII (9) complexes, which show a 3D lvt network for 6 and 7, a 2D (4,4) layer for 8, and a 3D (3,5)-connected (4·62)(4·67·82) network for 9. These results demonstrate that the diverse coordination motifs for 1–9 (from 0D, 1D, 2D, to 3D) can be effectively adjusted by the metal-ligating tendency and metal-dependent counter-anion effect. Thermal stability and solid-state fluorescence have also been investigated.
- This article is part of the themed collection: International Year of Crystallography Celebration: Asia-Pacific

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...