Molecular dynamics simulations of the interaction of citric acid with the hydroxyapatite (0001) and (011ˉ0) surfaces in an aqueous environment
Abstract
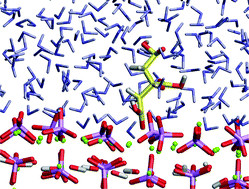
Molecular dynamics simulations are employed to investigate the adsorption of ![[1 with combining macron]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_0031_0304.gif) 0) surfaces of hydroxyapatite. An aqueous environment is added through the explicit introduction of
0) surfaces of hydroxyapatite. An aqueous environment is added through the explicit introduction of ![[1 with combining macron]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_0031_0304.gif) 0) surfaces respectively.
0) surfaces respectively. ![[1 with combining macron]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_0031_0304.gif) 0) surface and hence would inhibit growth of this surface more effectively than growth of the (0001) plane with which it does not interact strongly in an aqueous environment where the water competes with the citric acid for
0) surface and hence would inhibit growth of this surface more effectively than growth of the (0001) plane with which it does not interact strongly in an aqueous environment where the water competes with the citric acid for ![[1 with combining macron]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_0031_0304.gif) 0] direction in the presence of
0] direction in the presence of ![[1 with combining macron]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_0031_0304.gif) 0) surface in the hydroxyapatite morphology.
0) surface in the hydroxyapatite morphology.
- This article is part of the themed collection: CrystEngComm focuses on biomineralisation

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...