Distinguishing d- and l-aspartic and isoaspartic acids in amyloid β peptides with ultrahigh resolution ion mobility spectrometry†
Abstract
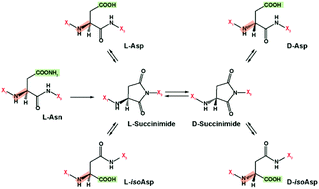
While α-linked amino acids in the L-form are exclusively utilized in mammalian protein building, β-linked and D-form amino acids also have important biological roles. Unfortunately, the structural elucidation and separation of these different amino acid types in peptides has been analytically challenging to date due to the numerous isomers present, limiting our knowledge about their existence and biological roles. Here, we utilized an ultrahigh resolution ion mobility spectrometry platform coupled with mass spectrometry (IMS-MS) to separate amyloid β (Aβ) peptides containing L-aspartic acid, D-aspartic acid, L-isoaspartic acid, and D-isoaspartic acid residues which span α- and β-linked amino acids in both D- and L-forms. The results illustrate how IMS-MS could be used to better understand age-related diseases or protein folding disorders resulting from amino acid modifications.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...