Direct oxidation of the C(sp2)–C(sp3) bond from benzyltrimethylsilanes to phenols†
Abstract
A novel pathway for direct conversion of benzylsilanes to phenols by oxidation with Na2S2O8 and oxygen is efficiently developed under mild and neutral conditions. The reaction shows good functional group tolerance to afford phenols in moderate yields. The possible mechanism is proposed based on the isotopic labeling trials.
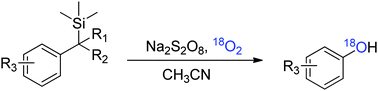


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...