Water-bridged hydrogen bond formation between 5-hydroxylmethylcytosine (5-hmC) and its 3′-neighbouring bases in A- and B-form DNA duplexes†
Abstract
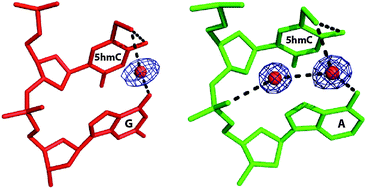
5-Hydroxylmethylcytosine (5hmC) has been recognized as the sixth base with important biological functions in many tissues and cell types. We present here the high-resolution crystal structures and molecular simulation studies of both A-form and B-form DNA duplexes containing 5hmC. We observed that 5hmC interacts with its 3′-neighboring bases through water-bridged hydrogen bonds and these interactions may affect the further oxidation of 5hmC.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...