Click chemistry-mediated catalytic hairpin self-assembly for amplified and sensitive fluorescence detection of Cu2+ in human serum†
Abstract
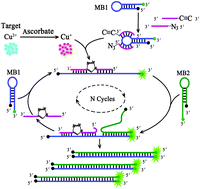
Chemically reduced Cu2+ triggers the ligation of alkynyl- and azido-modified DNA via click chemistry. Subsequently, the ligated DNA initiates cyclic assembly of two fluorescently quenched hairpin DNAs and generates significantly amplified fluorescence signals for highly sensitive detection of Cu2+ in human serum samples.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...