Paramagnetic relaxation based biosensor for selective dopamine detection†
Abstract
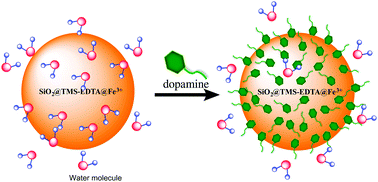
We report a new NMR relaxation time-based method for sensitive and selective dopamine detection using paramagnetic nanoparticles. The Fe3+ species in the nanoparticles serves as both the contrast agent and the target recognition element. The results demonstrate that paramagnetic nanoparticles, similar to the more widely used superparamagnetic nanoparticles, can be integrated into relaxation based detection schemes while avoiding the aggregation problem commonly associated with superparamagnetic nanoparticles.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...