Visible-light photodecomposition of acetaldehyde by TiO2-coated gold nanocages: plasmon-mediated hot electron transport via defect states†
Abstract
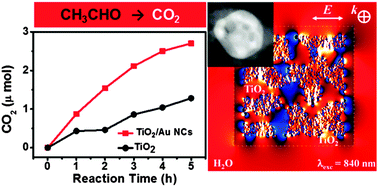
Skeletal gold nanocages (Au NCs) are synthesized and coated with TiO2 layers (TiO2–Au NCs). The TiO2–Au NCs exhibit enhanced photodecomposition activity toward acetaldehyde under visible light (>400 nm) illumination because hot electrons are generated over the Au NCs by local surface plasmon resonance (LSPR) and efficiently transported across the metal/semiconductor interface via the defect states of TiO2.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...