Chloride-assisted catalytic water oxidation†
Abstract
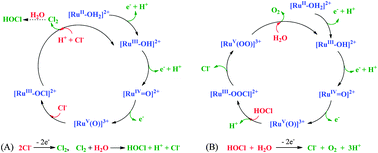
Rates of electrocatalytic water oxidation to oxygen by Ru(II) polypyridyl complexes are enhanced by added NaCl. Observations based on the single-site catalyst [RuII(Mebimpy)(bpy)(OH2)]2+ (Mebimpy is 2,6-bis(1-methylbenzimidazol-2-yl)pyridine; bpy is 2,2′-bipyridine) at pH 7.0 in a phosphate buffer suggest a mechanism involving initial oxidation of the catalyst to RuV(O)3+ followed by Cl− oxidation to HOCl. Once formed, HOCl is oxidized to O2.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...