sp3C–H bond alkylation of ketones with alkenes via ruthenium(ii) catalysed dehydrogenation of alcohols†
Abstract
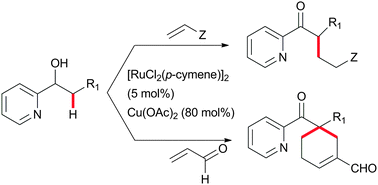
The sp3C–H bond functionalisation of 2-pyridyl ethanols upon reaction with alkenes, in the presence of a [RuCl2(arene)]2 catalyst and Cu(OAc)2·H2O, is performed under mild conditions without additional base. This reaction proceeds via a tandem alcohol dehydrogenation/alkylation with alkenes of the resulting ketone at its α sp3C–H bond.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...