In situ111In-doping for achieving biocompatible and non-leachable 111In-labeled Fe3O4 nanoparticles†
Abstract
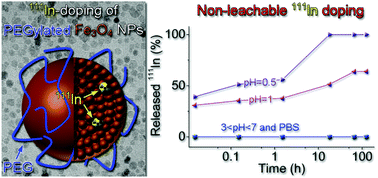
The present study reports a new approach for synthesizing 111In-radiolabeled biocompatible Fe3O4 nanoparticles. Radioactive 111In is doped in situ into the lattice of Fe3O4 nanoparticles to achieve robust radiolabeling for accurately tracing PEGylated Fe3O4 particles in vivo.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...