Circular permutation of E. coli EPSP synthase: increased inhibitor resistance, improved catalytic activity, and an indicator for protein fragment complementation†
Abstract
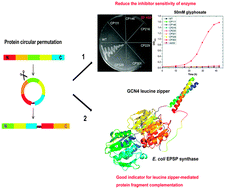
We performed the first circular permutation analysis for E. coli 5-enolpyruvylshikimate-3-phosphate synthase, and identified one circular permutant with notably increased resistance to its specific inhibitor and several others with moderately improved catalytic activity. Valid circular permutation sites can be used as effective split sites of protein fragment complementation.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...