Bilirubin oxidase bioelectrocatalytic cathodes: the impact of hydrogen peroxide†
Abstract
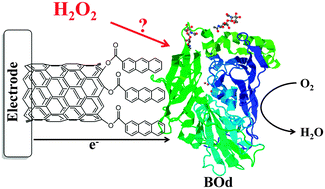
Mediator-less, direct electro-catalytic reduction of oxygen to water by bilirubin oxidase (Myrothecium sp.) was obtained on anthracene-modified, multi-walled carbon nanotubes. H2O2 was found to significantly and irreversibly affect the electro-catalytic activity of bilirubin oxidase, whereas similar electrodes comprised of laccase (Trametes versicolor) were reversibly inhibited.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...