Organocatalysed decarboxylative protonation process from Meldrum's acid: enantioselective synthesis of isoxazolidinones†
Abstract
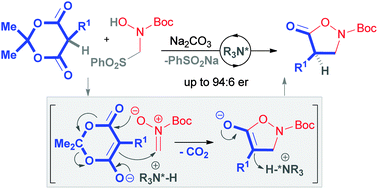
An asymmetric organocatalysed decarboxylative protonation reaction allowed a straightforward synthesis of α-substituted isoxazolidin-5-ones from readily available 5-substituted Meldrum's acids. This process is initiated by an anionic formal (3+2) cycloaddition–fragmentation, generated in-situ from a sulfone-amide precursor which also served as a latent source of proton.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...