Programmable hydrogels for the controlled release of therapeutic nucleic acid aptamers via reversible DNA hybridization†
Abstract
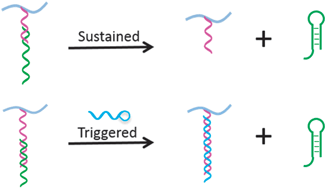
Reversible DNA hybridization can be used as a new mechanism to control the sustained and triggered release of therapeutic oligonucleotides from hydrogels.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...