An aqueous rechargeable lithium battery of high energy density based on coated Li metal and LiCoO2†
Abstract
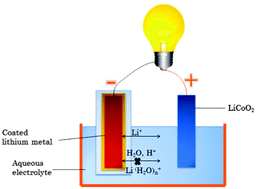
Using a coated Li metal as an anode and LiCoO2 as a cathode, an aqueous rechargeable battery is built up, whose average discharge voltage is 3.70 V. This high voltage stability is due to the “cross-over” effect of Li+ ions, which is different from the traditional ways of increasing overpotentials. The total energy density can be 465 W h kg−1.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...