Phosphoester-transfer mechanism of an RNA-cleaving acidic deoxyribozyme revealed by radioactivity tracking and enzymatic digestion†
Abstract
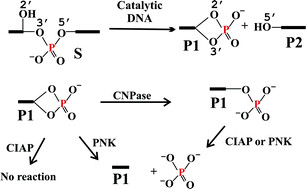
A convenient method involving 32P-labeling of an RNA substrate at the cleavage site and subsequent enzymatic digestion of cleavage products via phosphatases reveals that pH4DZ1—an RNA-cleaving deoxyribozyme with optimal activity at pH 4—forms a 5′-cleavage fragment with 2′,3′-cyclic phosphate group and a 3′-cleavage fragment with 5′-OH group.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...