Adaptive immune cells are necessary for the enhanced therapeutic effect of sorafenib-loaded nanoparticles
Abstract
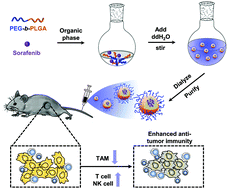
Sorafenib is a kinase inhibitor approved for the treatment of primary kidney cancer, advanced primary liver cancer, and radioactive iodine resistant advanced thyroid carcinoma. However, sorafenib usually causes serious side effects, which limit its antitumor effect. Nanoparticle based drug delivery systems have been widely used to enhance the therapeutic effects and reduce the side effects of this drug by the enhanced permeability and retention (EPR) effect. Herein, to improve the therapeutic effect of sorafenib, we developed poly(ethylene glycol)-b-poly(lactic acid-co-glycolic acid) (PEG-PLGA) based nanoparticles by a dialysis method for sorafenib encapsulation. After intravenous injection of the sorafenib loaded nanoparticles (NPsorafenib), the tumor growth of mice bearing B16-F10, MC38 and LLC tumor was significantly inhibited. Meanwhile, the dose of sorafenib was reduced to one ninth and the side effects on the hematopoietic system and immune system were abrogated. More importantly, the tumor growth inhibition effect of NPsorafenib was dramatically reduced in B16-F10 bearing Rag1−/− mice which are adaptive immune cell defective, indicating that the antitumor effects of NPsorafenib are dependent on the adaptive immune cells. These results emphasize the indispensable role of the adaptive immune system in nano-drug mediated antitumor effects and the adaptive immune system should be considered as an important factor for clinical applications.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...