Enzyme/pH-sensitive polyHPMA–DOX conjugate as a biocompatible and efficient anticancer agent†
Abstract
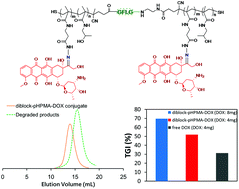
In this study, to enhance the therapeutic function and reduce the side-effects of doxorubicin (DOX), a biodegradable N-(2-hydroxypropyl) methacrylamide (HPMA) polymer–DOX conjugate has been prepared through reversible addition fragmentation chain transfer (RAFT) polymerization and conjugation chemistry, and the anticancer agent DOX was covalently linked to the polymeric vehicle through a pH-responsive hydrazone bond. The cellular mechanisms of the conjugate were explored, and the therapeutic indexes were studied as well. The high molecular weight (MW) polymeric conjugate (94 kDa) was degraded into products with low MW (45 kDa) in the presence of lysosomal cathepsin B and also showed pH-responsive drug release behavior. In vitro cellular mechanism studies revealed that the polymeric conjugate was uptaken by the 4T1 cells, leading to cell apoptosis and cytotoxicity to cancer cells, while the polymeric conjugate demonstrated excellent in vivo biosafety even at a high dose. Compared to free DOX, the conjugate has a much longer half-life in pharmacokinetics and accumulates in tumors with a much higher amount. The conjugate therefore has a much greater in vivo anticancer efficacy against 4T1 xenograft tumors and shows subtle side-effects, which were confirmed via tumor size and weight, immunohistochemistry and histological studies. Overall, this polymeric conjugate may be used as an enzyme/pH-sensitive anticancer agent.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...