Novel poly(vinyl alcohol)-based amphiphilic nanogels by non-covalent boric acid crosslinking of polymeric micelles†
Abstract
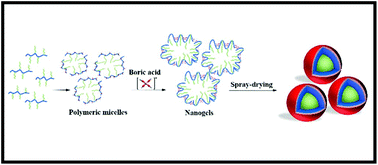
In this work, we report a new type of poly(vinyl alcohol)-g-poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) (PVA-g-PNiPAAm) amphiphilic nanogel produced by the non-covalent crosslinking of PVA polyol domains in preformed polymeric micelles with boric acid. The nanomaterials showed sizes in the 100–250 nm range (DLS) and a spherical morphology (HR-SEM). We demonstrated that the size of the polymeric micelles could be fine-tuned by changing the concentration (and the aggregation pattern) of the polymeric amphiphile in water. Upon crosslinking, the polymeric micelles turned into physically stable amphiphilic nanogels that displayed both size and size distribution similar to the micellar precursor for up to two weeks, even under disfavored conditions of concentration and temperature that, in the case of non-crosslinked counterparts, resulted in quick disassembly. In addition, we show for the first time the feasibility of spray-drying technology to consolidate the 3D network formed between PVA and boric acid and to produce stable powders that can be reconstituted upon use at any desired concentration. Moreover, the formation of a borated surface conferred the nanogels with good mucoadhesiveness in vitro. Finally, these novel nanomaterials showed optimal cell compatibility in a model of the intestinal epithelium, the Caco2 cell line. Overall results demonstrate the unprecedented versatility of the proposed modular approach and opens completely new horizons in the application of polymeric micelles and other self-assembled polymeric nanomaterials in diagnostics and therapeutics.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...