Effects of nanoparticle surface ligands on protein adsorption and subsequent cytotoxicity†
Abstract
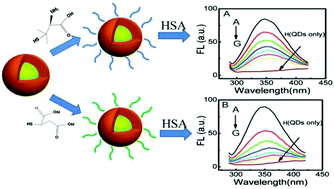
With the widespread use of nanoparticles (NPs) such as quantum dots (QDs) in biomedical applications, and the growing concerns about nanotoxicity of these engineered nanoparticles, the importance of nanoparticle–protein interaction has not been well emphasized. In order to better understand the physical basis of the biological activity of nanoparticles in nanomedicine applications or under conditions of environmental exposure, the interaction of CdSe/ZnS QDs having different surface ligands as a model with human serum albumin (HSA) has been investigated in detail by various spectroscopic techniques including UV-vis absorption, fluorescence, circular dichroism, and Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopies. We find that QDs coated with zwitterionic D-penicillamine (DPA-QDs) or anionic mercaptosuccinic acid (MSA-QDs) bind to the same site of serum albumin, domain II A, site I, and the differences of the Stern–Volmer quenching constant KSV and the binding constant K are about sixfold and sevenfold after 4 h of mixing, respectively. We also find tentative evidence that the model proteins undergo conformational changes upon association with the QDs that have different surface ligands. Additional cellular cytotoxicity assays, with HeLa cells, reveal that the stronger adsorption capacity of HSA on the surface of MSA-QDs results in more reduced cytotoxicity for the protein-coated QDs, while the weaker binding capacity of HSA on DPA-QDs has less effect on the interaction of QDs with cells. These findings have shed light on the design and application of QDs nanomaterials to nanomedicine by a comprehensive preconsideration of their interaction with human serum proteins.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...