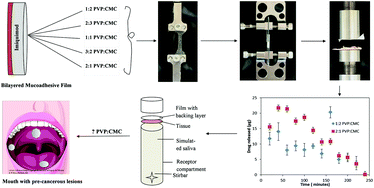
Oral mucosal delivery has gained prominence in the last two decades because the rich vasculature of the tissue enables rapid delivery and avoidance of first pass metabolism. Although commercial mucoadhesives are used for systemic delivery, systems are not currently available for treatment of local conditions. In the present work, mucoadhesive films are being developed for locally controlled release of an immune response modifier for preventing precancerous lesions from progressing to oral squamous cell carcinoma. Previous research showed that films composed of polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP) and carboxymethylcellulose (CMC) released imiquimod in a sustained manner for 3 h. In continuing development of the system, additional key properties were investigated with changes in composition. While adhesive properties in pull-off (0.42 ± 0.03 to 1.1 ± 0.1 N cm−2) and shear adhesion (1.7 ± 0.25 to 5.6 ± 1.4 N cm−2) increased with increasing PVP content of films, tensile properties, such as modulus (6.9 ± 1.5 to 1.8 ± 0.2 MPa) and ultimate strength (4.2 ± 0.7 to 2.1 ± 0.02 MPa), decreased as PVP content increased. Release profiles of the films showed that an increased PVP content resulted in burst release and faster erosion compared to sustained release and slower erosion with more CMC. Studies of transport kinetics showed that the films doubled the amount of imiquimod localized within epithelium compared to drug in solution, increasing their potential for local treatment of oral dysplasia. The mucoadhesive drug delivery system based on CMC and PVP offers a wide range of these properties without addition of new constituents.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...