TiO2/CdS nanorod array-based photoelectrochemical sensing of Cu2+ in human serum samples
Abstract
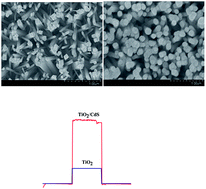
In this study, we report a sensitive and selective photoelectrochemical sensor for the detection of Cu2+ in human serum samples based on a TiO2/CdS nanorod array. To prepare the sensor, a TiO2 nanorod array was initially deposited onto a fluorine-doped tin oxide (FTO) conductive glass, and then, CdS nanoparticles were deposited onto the TiO2 nanorod array surface. The well-matched energy level between TiO2 nanorod and CdS efficiently suppressed the recombination of photogenerated electron and hole (e−/h+) pairs; this led to improved photon-to-current conversion efficiency. Experimental results demonstrated increased photoelectrochemical current of TiO2/CdS as compared to that of TiO2 alone. Utilizing the interaction between Cu2+ and CdS, the constructed photoelectrochemical sensing platform shows selective response towards Cu2+. Increased Cu2+ ion concentration resulted in the decreased photoelectrochemical current intensity, and a linear range of 1 nM to 1 μM was obtained with a detection limit of 0.5 nM. Due to its good performances, the sensor was successfully applied for the direct detection of Cu2+ in human serum samples, and the results suggested the potential of this sensor for practical clinical applications.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...