Highly sensitive electrochemical detection of mercuric ions based on sequential nucleic acid amplification and guanine nanowire formation†
Abstract
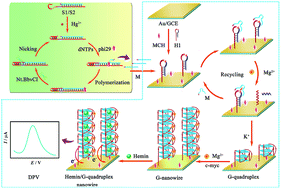
The selective and sensitive detection of mercuric ions (Hg2+) is of great significance in environmental protection and disease prevention. By integrating target induced strand displacement amplification (SDA) and metal ion-dependent DNAzyme cyclic amplification to grow guanine nanowires (G-nanowires) as the signal output component, we demonstrate here a label-free and sensitive strategy for Hg2+ detection. The target induced SDA can amplify a large amount of Mg2+-dependent enzymatic sequences, which can be further hybridized with a hairpin-structured substrate that contains a G-quadruplex sequence to form Mg2+-dependent DNAzymes. In the presence of Mg2+, the Mg2+-dependent DNAzymes exhibit high catalytic activity and excellent cleavage specificity toward the substrate sequences, releasing the enzymatic sequences to trigger another cleavage cycle and leaving the G-quadruplex fragment on the electrode surface for the formation of G-quadruplex/hemin repetitive units. With the enzyme/DNAzyme for signal amplification and the G-quadruplex/hemin for signal generation, the electrochemical assay for Hg2+ detection shows excellent sensitivity for a concentration variation from 0.2 pM to 100 nM with a detection limit of 0.097 pM and is successfully used in the direct detection of real water samples with high sensitivity and selectivity.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...