A rapid and sensitive turn-on fluorescent probe for ascorbic acid detection based on carbon dots–MnO2 nanocomposites†
Abstract
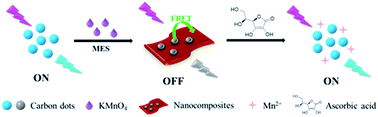
Ascorbic acid (AA) is a significant small biomolecule and plays a key role in many biochemical processes. In this work, a rapid turn-on fluorescent probe was developed for sensitive and selective sensing of AA based on carbon dots–MnO2 nanocomposites. The nanocomposites were constructed by in situ synthesis of MnO2 nanosheets in carbon dot (C-dot) solution, and the fluorescence of C-dots was quenched with the formation of the nanocomposites due to the fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET) from C-dots to the generated MnO2 nanosheets. Once AA was introduced into the system, MnO2 nanosheets were reduced to Mn2+ and the fluorescence of C-dots would be recovered. Under the optimized conditions, this method shows rapid and sensitive response toward AA, the assay time is 2 min and the limit of detection is 68 nM. Moreover, the carbon dots–MnO2 nanocomposite based fluorescence sensing system was successfully employed to determine AA in commercial tablets with satisfactory results. Taking full advantage of C-dots and MnO2 nanosheets, this probe shows remarkable properties including easy operation, low cost and good biocompatibility, and has great potential to be used in biological and clinical diagnostic applications.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...